|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Electronic Article SurveillanceDeactivation System
|
|
|
Have a piece of cake… Build your own EAS /
Detection / Deactivation System… It is Easy… It is Fun…

Introduction:
The
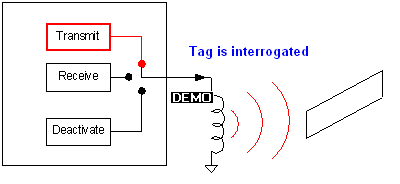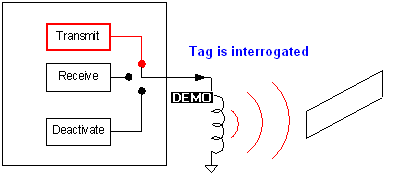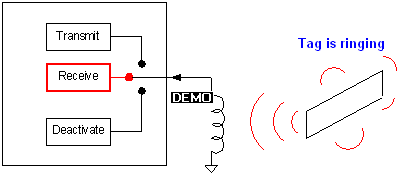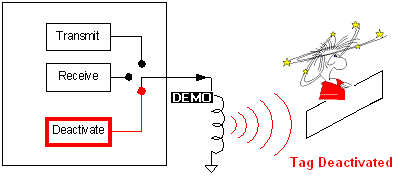
EAS system detects a tag by ringing it and listening to it’s ringing (this is interrogation),
once validated the fingerprint of its reply it is then deactivated if required.
The
Deactivation system is mainly composed of the following simple elements:
1.
Power:
Main Power with isolated and filtered terminals. Since there are various
frequencies generated internally and they unit may be susceptible to external
interference an EMC filter is required. Also unit requires immunity against
conductive and reradiated emissions.
2.
Capacitor Charger: This circuit controls and initiate the charging of a high microfarad
value cap to a maximum of about 500 volts DC. The DSP/MCU controls and monitors
this circuit for optimum response and can be also controlled via a computer
interface circuit.
3.
Deactivation Control: It is a switch like simple circuit that allows or
disallows the high current voltage pressure stored in the large cap to be
vented to the antenna circuit. This control circuit is activated via the
MCU/DSP as well.
4.
Antenna: The same antenna is shared for use by the detection circuit
(Transmitter & Receiver) and the Deactivation (High voltage cap) circuits.
5.
CPU/DSP: Is a relatively high-speed controller that is capable of handling all
of functionalities illustrated below. This is the main brain of the system.
Many processors are available in the market palce that have high pin count for
handling different signals and peripherals. Among the famous chip providers are
Texas Instruments, Free Scale, Analog Device, Microchip, Seiko, Philips, NCR,
Zialog, Rabbit, Renesas, and other.
6.
Transmitter: The transmitter transmits a 58 KHz signal that can only reach certain
region (Detection Zone). If the tag is located within this zone it will then
rings and reply back to the antenna of the EAS system.
7.
Receiver: It receives the reply back of the tag when it rings. At the same time
it will listen to any frequency in the detection zone but will then be filtered
(eliminated) internally. Only signals of 58 KHz frequencies will be passed to
the internal circuit, conditioned, and processed by the CPU/DSP firmware.
8.
Isolation Cap: Is a filtering capacitor used to enable the Transmitter, Receiver, and
the Deactivation circuits all share the same antenna. Without this Isolation
tuning Cap the high power of the Deactivation circuit will blow up the
Transmitter and/or Receiver circuits.
9.
Antenna: This antenna is shared among all the Deactivation, Transmitter, and
Receiver circuits. It is optimized to operate for both the Detection 58 KHz
(Transmit & Receive) and the Deactivation high energy 500 Hz. It is
basically a high AWG gauge cooper wire winded on a ferrite element to produce
as high output power as possible. Some EAS systems have the antenna made of
only wire winded on an air core coil. Other EAS system have this antenna made
of only the copper traced on the PCB to preserve on space and power transmitted
since a battery is used for the hand held EAS systems. The Impedance of the
antenna is designed in such, as it will see almost matching impedance to all of
the Deactivation, Transmit, and Receive circuits.
10. Interface GPIO: A set of Input/Output ports used to
interface the EAS system to other peripherals such as the Point Of Sale (POS),
LAN Ethernet connection, RS232, RS485, GPIOs, or other.
11. Program Button: One or more buttons used to handle error or
reset conditions, make various system parameters selections, or system
synchronization.
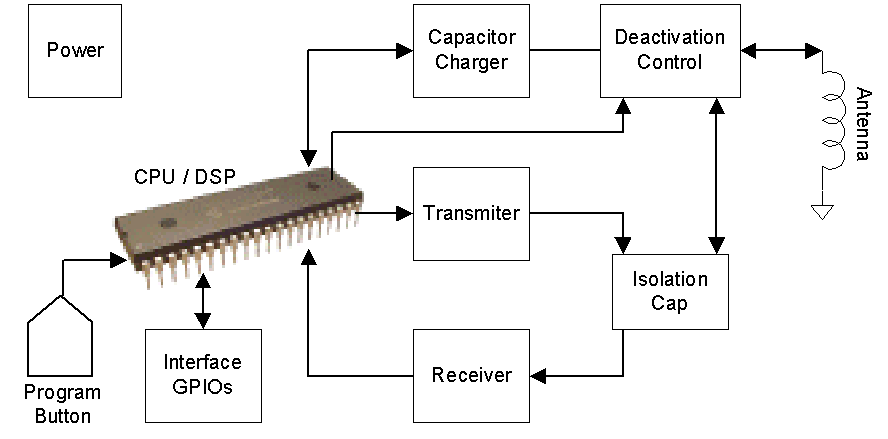
Detailed Block
Description
Algorithm:
Schematics:
|
________________________________________________________________________________ |
|
EAS > Page 1 Page 2 Page 3 |
By: Engr. Firas Faham, P. Eng., C. Eng.,
B. Eng.
20+ years extended experience in the
design of Automatic Electronic Systems

